What is Artificial Intelligence?

Artificial Intelligence, especially Machine Learning, is the technology behind disruptive businesses like Uber, Airbnb, or Amazon. As I mentioned in a post a few months ago: “Artificial Intelligence is the new electricity”.
In this post, I aim to answer basic questions for non-technical people such as: what is it?, what types are there?, what can we do with it?, or what can we expect in the future?
WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?
To start, simplifying a lot, we can say that Artificial Intelligence (especially Machine Learning) is a new way of generating software in which we do not use the traditional method (programming a machine through instructions) but let the machine learn through data.
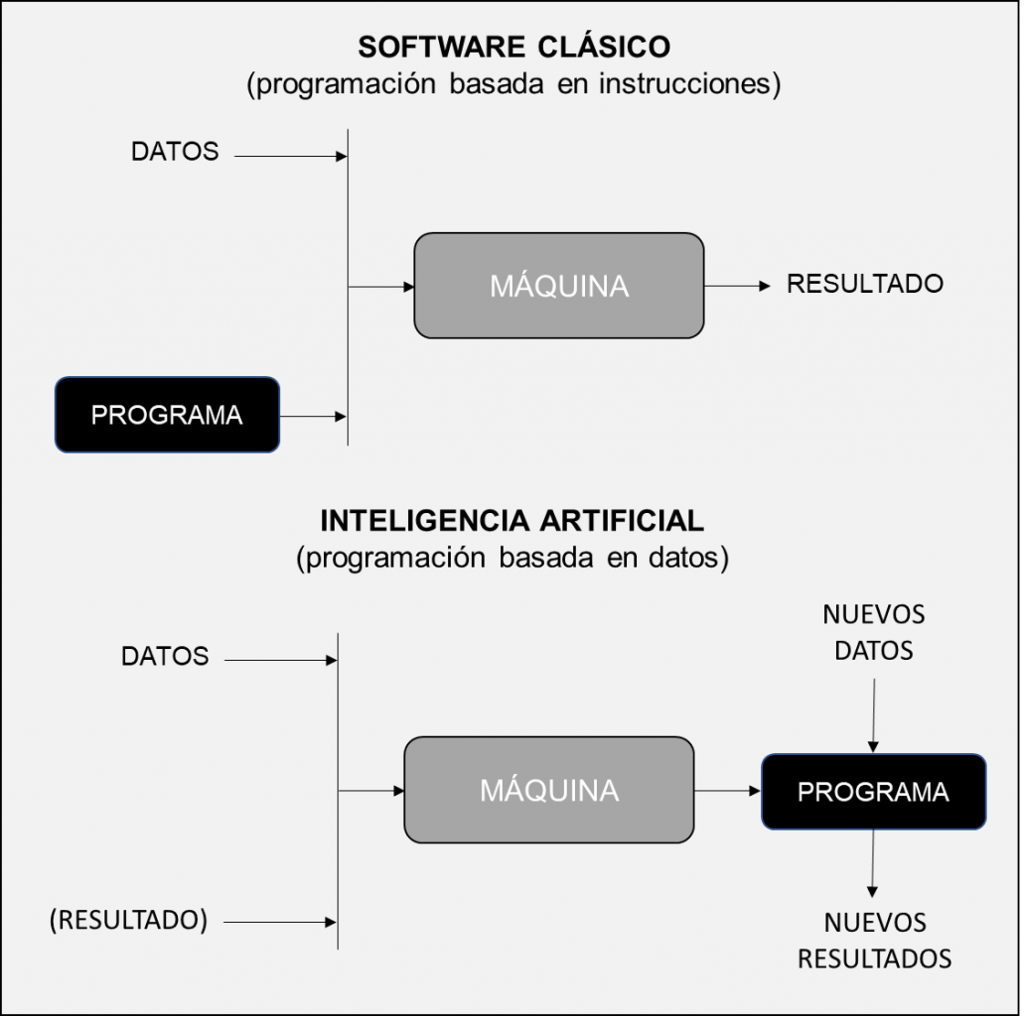
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
If we want a classic definition, we can rely on the one John McCarthy used when he first introduced the term Artificial Intelligence in 1956:
“Artificial Intelligence is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs.”
John McCarthy
Previously, in 1950, Alan Turing wondered if machines could think (“Can machines think?”). Artificial intelligence is the technology that allows machines to think and make decisions without human intervention. It is not about programming a computer in the traditional way to react to a predefined fact, but to show signs of human intelligence such as the ability to learn.
WHAT TYPES OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE EXIST?
Although science fiction has insisted on presenting us with Artificial Intelligence capable of performing any task as well as or better than a person, the reality is different. The intelligent systems that exist are defined to solve specific problems. According to their level of generalization, we can classify artificial intelligence into:
- Weak Artificial Intelligence is only capable of acting in a specific domain of knowledge (for example, predicting product demand, recommending movies, or driving). It is the most mature at this moment and is used in all kinds of scenarios, including Siri, search engines like Google, chatbots, translators, etc.
- General Artificial Intelligence is capable of performing any human task with the same level of efficiency as us. Thanks to this intelligence, machines would have the ability to solve any type of problem. It does not exist.
- Super Artificial Intelligence or Strong AI surpasses in all aspects the limits of human intelligence. This type of AI does not exist beyond science fiction movies in which, in addition, they are aware and capable of feeling emotions and acting based on them as people do.
Weak Artificial Intelligence is already present in our lives without us being aware of it. The rest are the objective of the most ambitious research, and although their existence may be distant, if they ever exist, we must not forget that:
“The only way to discover the limits of the possible is to venture a little way past them into the impossible.”
Arthur C. Clarke
WHAT CAN WE DO WITH ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?
In a very simple way, we can consider that Artificial Intelligence allows:
- Learning. As I described earlier, without the need for explicit programming.
- Understanding. Being able to classify, recommend, or make predictions based on input data. All our interactions with digital platforms and stores (for example, Amazon) use AI to personalize our experience, predict our behavior, and recommend the most suitable products.
- Perceiving. Being able to extract information from images or videos (computer vision), sounds, or texts. Some examples are facial recognition systems or personal assistants like Amazon Alexa.
- Acting. Making decisions and acting autonomously accordingly. From the Roomba robot that cleans your house to some credit scoring systems, its use is more common than it seems.
Next, I will delve into machine learning: MACHINE LEARNING.
WHAT IS MACHINE LEARNING?
Machine Learning is the branch of Artificial Intelligence that uses algorithms to build systems with the ability to learn and improve from experiences without being explicitly programmed. In this branch of AI, the result no longer depends on rules and a programmer, but the system is able to establish its own rules through training.
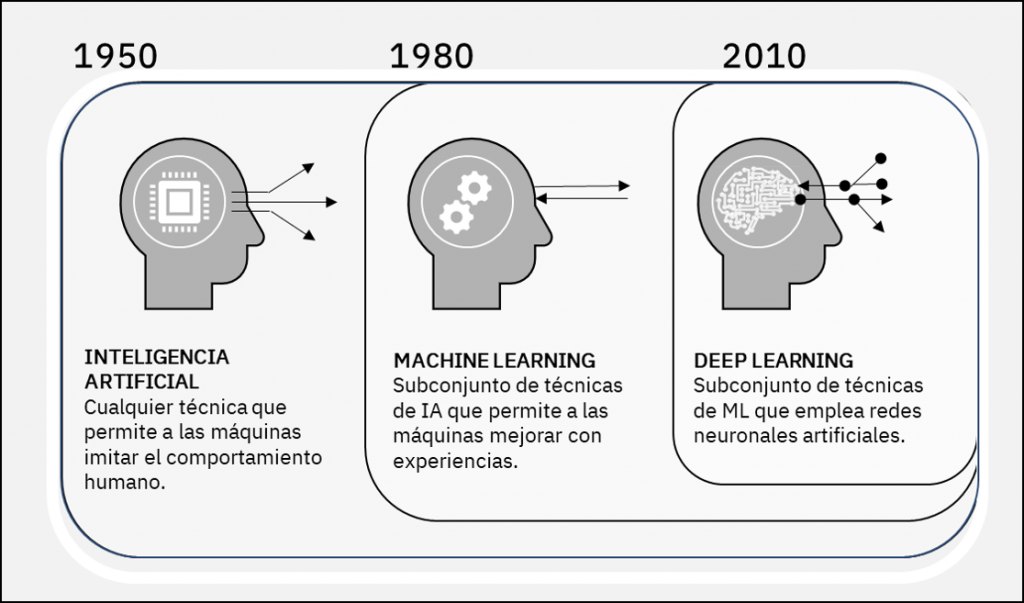
Unknowingly, we are using them when Amazon or a Social Network recommends what may interest us, or Netflix new movies or series to watch, when we search for a term on Google, when we use voice assistants like Siri, when the browser suggests the best route to our destination, etc. It is an omnipresent technology that surrounds us and impacts our daily decisions without us sometimes being able to recognize it.
When we train algorithms based on a dataset that includes both input variables and results, it is called Supervised Learning. For example, a product price prediction system should be trained with a price history and the set of associated environmental variables (sociodemographic variables, macroeconomic variables, etc.) The system will learn from past events (relationship between variables and prices) to predict the future outcome when we only have the variables.
In Unsupervised Learning, we do not have a set of labeled data (results along with input variables), so the algorithm learns by detecting patterns without the need for anyone to supervise it. It is widely used in identifying anomalous transactions or fraudulent behaviors.
In Reinforcement Learning, the system learns from interacting with the environment with a continuous trial and error approach. The algorithm will make decisions based on the training data, and we must give it feedback with rewards and punishments depending on whether the result is as expected or not. In this way, the system learns from our response, based on receiving rewards or punishments. Its use is growing in any environment where it interacts with humans since people can sometimes, unknowingly, train the algorithm by rewarding or punishing it for its successes and errors.
WHAT IS DEEP LEARNING?
Deep Learning is a Machine Learning technique inspired by how our brain works with layers of connected neurons. Each neuron is specialized in solving a type of problem, and data processing occurs in cascade.
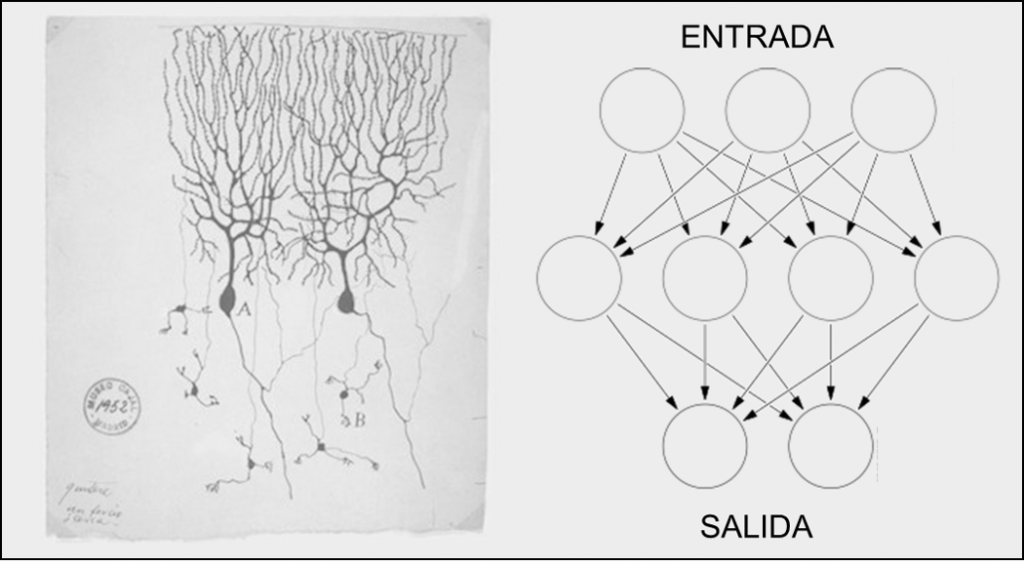
Since its introduction, data passes through the different layers where learning rules are applied, and they are modulated by weights. During training, the results of the last layer are compared with the correct results, allowing the system to adjust the weights. Once the system has learned, the weights are considered final.
Deep Learning has been used, for example, in creating image search algorithms, automatic translation systems, or automatic subtitle generation. It is the key technology behind applications like autonomous cars, allowing them to recognize signals, detect other vehicles, pedestrians, etc.
WHAT CAN WE EXPECT FROM ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?
In February 2018, the MIT Technology Review released its annual list of “10 breakthrough technologies” which included “Dueling Neural Networks” and “AI for Everybody.” In the latter, the article highlights the importance of making Artificial Intelligence accessible to all companies and all people so that not only big tech companies have access to it. This is already happening and is one of the reasons why we can expect, as Andrew Ng said, it to become the new electricity.
Unaware of its presence, AI is already the enabler of the rest of technological advances.
If in 2011, HP executive and investor Marc Andreessen coined the phrase “Software is eating the world,” 6 years later we can paraphrase it by saying:
“Artificial Intelligence is going to eat the world”
REFERENCES
- Artificial Intelligence is the new electricity
- Artificial Intelligence
- John McCarthy, the start of artificial intelligence
- 10 breakthrough technologies

DEPECHE MODE
Whenever I think of autonomous vehicles (and therefore Artificial Intelligence), this song comes to mind. I leave you with it: “Behind the Wheel” by Depeche Mode.
Related posts
From COBOL to Agentic AI: Transforming the Software Lifecycle
Evolution of the software lifecycle applying AI and Agentic AI

Digital Transformation: Beyond Technology
In Digital Transformation, purpose and culture are more important than technology itself.

BIG TECH CAPITALISM by Evgeny Morozov
'Big Tech Capitalism' shares many of the issues I describe in 'The End of Inertia' but does not approach them in the same way, as its author starts from an e...
All opinions expressed on this blog are personal and do not represent those of any company or organization with which I collaborate.

